
To every mother, child caregiver, teacher, every mother-to-be, or trying to conceive, first aid is the most important thing to know in order to deal with children.
Children always seek discovery, approaching electrical wires thinking it is (Disneyland)!
Therefore, knowing first aid may save a child’s life and prevent any complications.
Let’s review together different situations and how to perform first aid.
First aid for children with fever
Mothers go through this often; Particularly with children at a young age, due to infection, especially during the teething period.
Here are the most important things you can do:
- Make sure the child drinks fluids and water to avoid dehydration.
- Make sure the child wears light clothing.
- Bathing the child with lukewarm water helps to reduce the temperature.
- Make sure to take the temperature regularly.
- Give the child antipyretics according to the doctor’s instructions.
Get help immediately
Get immediate assistance if the child is;
- Not responding.
- Breathing with difficulty.
- Convulsing.
- Less than three months old, and has a temperature higher than 38 ℃.
- Suffering a temperature of 40 ℃ or more that continues for more than 24 hours.
- Vomiting has diarrhea, or signs of dehydration, such as a dry mouth.
- Feverish with a rash.
- More susceptible to infection than others because of an immune or blood disease,
- Did not receive his immunizations.
- The soft spot in the child’s skull is swollen.
First aid for children when they choke
A child may suffocate by swallowing an object that has blocked the airway, such as a toy.
Additionally, a child can also suffocate due to vomiting as a result of GERD.
We can address this topic according to the age of the child.
If the child is less than a year old
If the child is less than a year old, the first aid for infants is as follows:
- Sit in a comfortable place, and hold the child on your arm so that his head is in the palm of your hand, and fix the child’s head well, then put your hand on your thigh as shown in the picture.
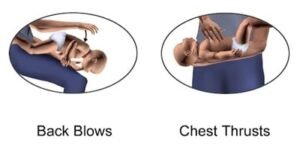
- Gently but firmly thump the middle of the child’s back, between the shoulders, five times with the heel of your palm. It will help expel the object suffocating the child.
- Check the child’s breathing. If he is not breathing, press two fingers into the middle of the chest to give five chest compressions. Examine the child’s breathing by bringing your ear close to his nose or mouth. This, should not exceed a few seconds. Repeat the aforementioned steps until help arrives.
If the object that caused choking has come out but the child still can’t breathe, you need to perform CPR.
If the child is over a year old
For children over one-year-old, we do the following:
- Thump the back with the heel of your palm five times. If the object blocking the airway does not come out, proceed to the next step.
- Stand facing the child’s back and with a closed fist apply pressure inward and upward, as if you were carrying the child from behind, and repeat five times as shown in the picture.
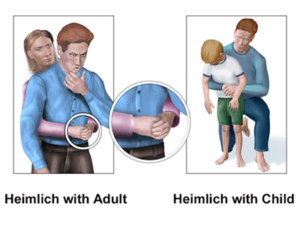
- If you’re not successful in opening the airway, repeat the previous steps in order until help arrives.
First aid for children when drinking chlorine
Many of us ask about first aid for children when they drink chlorine, in swimming pool water.
However, most problems occur upon drinking chlorine used as a detergent for house cleaning.
Here are some of the most important things you can do:
- Avoid helping the child vomit.
- Help the child drink plenty of milk or water right away unless there is vomiting or convulsions.
- Take your child and the bottle they drank into a poison center immediately.
First aid for children in the event of a fall
Many children fall, either because of their excessive movement or due to exploring their surroundings.
Therefore, we recommend that you know the following first aid tips:
- Check the child to make sure there are no cuts or injuries.
- Apply cold compresses to the bumps and bruises.
- Monitor your child and note any changes that may occur over the next 24 hours, such as:
- Vomiting more than once.
- Pain in the neck, back, or neck.
- Pain that increases with time.
- Difficulty walking
- Difficulty focusing his eyes.
- Any strange behavior.
This first-aid technique is considered one of the most important for infants due to their sudden new movements, lack of balance, and love of exploration.
If the child suffered a severe injury to the head, neck, back, or thigh bones, avoid moving him and call 911.
First aid for children with burns
Children can be at risk of burns from spilling a hot drink or something else, so here’s what to do:
- Help the child undress unless the clothes are sticking to the burn.
- Place the burn under lukewarm running water to reduce pain.
- Apply Vaseline gauze to the burn site.
- Do not open bubbles formed by the burn.
- Be sure to seek help if the burn covers a large area, is the result of an electric shock, or if it shows any signs of infection such as pus, etc.
First aid for children when electrocuted
Make sure you are safe and cut off electricity before you start helping.
You can use an electrical insulator to separate the child from the electrical current, such as any wood or plastic tool to isolate electricity.
Then follow the following precautions:
- Begin CPR if the child is not breathing or has no pulse. (Perform 100 uninterrupted hand compressions on the chest, and if you are CPR trained, press the chest 30 times before giving two rescue breaths. However, this method does not apply to newborns.).
- Try to keep the baby warm by covering him.
- If the electrocution causes burns, avoid covering them with a blanket so that the blanket does not stick to the burn.
- Use Vaseline gauze to cover the burn.
- Call an ambulance or head to the ER immediately if the child has:
- Cramps.
- Severe burns.
- Breathing difficulty.
- Arrhythmia.
- Myocardial arrest.
- is unconscious.
First aid for children when experiencing convulsions
There are several types of convulsions.
Children may convulse due to a fever, low blood sugar or an electric shock, etc.
Here are the most important things you can do:
- Convulsions end within minutes, so observe the child.
- Avoid restricting the child’s movement during convulsions.
- Avoid giving the child water or anything to swallow until he is fully conscious.
- Calculate the time of the seizure.
- Have the child lay on his side during the seizure to prevent saliva from escaping into the airway.
- Ask for help.
Prevention is better than cure.
Always keep your children safe and ensure that those who look after them are qualified:
Here are some ideas:
- Make sure that the child does not stay feverish for a long time. Also, use an antipyretic and cold compress. In addition, make sure to see the pediatrician so you can find out the cause of the fever and treat it.
- Avoid toys and small items that children can swallow.
- Avoid toys that contain small parts that may fall apart with use.
- If your baby has GERD, make sure to elevate his back and head when sleeping with pillows.
- Make sure to store household cleaners in closed cabinets out of the reach of children.
- Do not place infants in high places.
- Make sure to put pillows around the little one when he sleeps.
- Prevent children from jumping on beds and tables.
- Make sure your child wears a safety helmet when cycling, etc.
- Head protecting cushions for young children have also appeared on the market to avoid head injury when learning to walk.
- Be careful not to put hot objects within reach of children. Moreover, avoid placing hot drinks on a table with a long tablecloth.
- Finally, ensure electrical sources in the home are inaccessible to children.
In conclusion, our children are our responsibility, and their safety is our primary objective.
To qualify for this, we need to learn first aid techniques.
We also have to spread awareness among our acquaintances and every person we trust with our children.
