Turner syndrome | Does it only affect women? | Symptoms and treatment.
Turner syndrome

Turner syndrome is the most common sex-related chromosomal abnormality.
Its manifestations start at an early age affecting the typical growth and development stages.
It also causes several chronic medical problems, as well as affecting the ability to conceive normally.
Read along so you can learn more about this disease, its causes, and methods of treatment.
What is Turner syndrome?
Turner syndrome is a genetic disorder that affects girls and women.
It is mainly caused by; a random variation in chromosomes before birth.
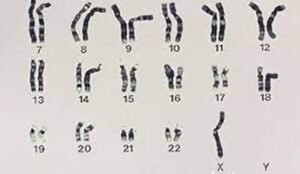
It results from the complete or partial loss of the X chromosome.
Girls are characterized by; short stature and premature ovarian failure.
Symptoms of Turner Syndrome
Affected females display some physical characteristics at birth and in their childhood, including:
- Short stature which is the hallmark of this syndrome, with an average adult height of 143 cm.
- Lack of normal sexual development: There are no menstrual periods and abnormal breast development, with a small ovary that may be active only for a few years or not at all.
- Swelling of hands and feet in infants.
- A particularly short wide neck. (webbed neck)
- Obesity
- Ptosis
- Flat feet
- Abnormal growth spurts since childhood
Females with this condition may also have other medical problems, including:
- Inability to conceive without medical intervention.
- Hearing loss.
- High blood pressure.
- Frequent ear infections.
- Kidney and urinary system diseases in about 30% to 40% of infected women.
- Cardiovascular problems, some of which may threaten their lives.
Does Turner syndrome cause complications?
Unfortunately, Turner syndrome exposes affected women to some medical problems and complications.
However, with proper monitoring and regular examinations, complications can be managed.
Possible medical conditions and complications include;
- Frequent urinary system infections.
- Kidney defects, which, may increase the risk of developing high blood pressure. (Hypertension)
- Hypothyroidism, Thyroid levels decrease.
- A higher than average risk of developing celiac disease. Such as allergy to foods containing gluten protein, like wheat and barley.
- Cardiac abnormalities are common; Therefore, a specialist should monitor affected people to avoid problems with the aorta and high blood pressure.
- Obesity can increase the risk of diabetes.
- Osteoporosis
- Difficulty learning
How common is Turner syndrome?
About 1 in 2,500 girls worldwide are born with Turner syndrome, the most common sex-related chromosomal abnormality in women.
Can this syndrome be prevented?
Unfortunately, nothing can be done to prevent it from happening.
It is a congenital problem that results from a random error in the X chromosome.
What are the types of Turner syndrome?
The type that a female suffers from depends on the type of problem in the X chromosome and is divided into;
- Classic: One of the X chromosomes is lost entirely, and this type affects about 45% of cases.
- Mosaic: One of the X chromosomes is partially missing, and this type affects about 30% of cases.
- Inherited: In rare cases, children inherit it from their parents, and this type usually occurs due to the loss of part of the X chromosome.
- X chromosome abnormalities: An abnormality or loss of parts of one of the X chromosomes occurs.
- Y chromosome genetic material: Some cells contain one X chromosome material, while some contain Y chromosome genetic material.
Diagnosis
Genetic testing, done before birth by taking a sample of amniotic fluid or the placenta, helps diagnose this syndrome.
A chromosomal analysis can also be performed, using a blood sample, to confirm a person’s genotype, and to detect if there are any genetic abnormalities in the chromosomes.
The medical history and clinical examination also contribute to the early detection of this syndrome.
Moreover, diagnosis allows parents to choose whether to terminate the pregnancy or follow-up and care for the child from a young age.
The doctor also orders tests to diagnose physical symptoms, including:
- Blood tests to check levels of female hormones.
- Heart defect examination.
- Ultrasound to examine the pelvis and kidneys.
- Chest magnetic resonance.
- Hearing tests.
- Eye check.
Turner syndrome and menstruation
The lack of menstruation in affected girls occurs due to the absence or impairment of ovarian function.
It occurs primarily due to a defect in the formation of the gonads or premature ovarian failure.
Some of them also need hormonal treatment to regularize the menstrual cycle.
Turner syndrome and marriage
Some studies have indicated difficulties in social functioning for affected women, as they differ from healthy women in having less interest in males and less sexual activity.
Studies have also shown that a small number of them enjoy a stable marriage.
Turner syndrome and pregnancy
Most infected women remain unable to have children or become pregnant through in vitro fertilization.
However, pregnancy involves many risks and requires close consultation with the patient’s health care team.
Male Turner Syndrome
This syndrome occurs only in females.
However, some disorders in males; are similar in presentation to Turner syndrome.
For example: having a short stature, drooping eyelids, and hormonal imbalance.
Turner syndrome and Klinefelter syndrome
They are genetic disorders caused by differences in the number of sex chromosomes.
Turner syndrome: occurs in 1 out of every 2500 female births due to the partial or complete absence of the X chromosome.
Klinefelter syndrome: occurs in 1 out of every 1,000 male births; As a result of an increase in the number of X chromosomes, it also results in osteoporosis and autoimmune disorders.
Turner syndrome treatment
There is no definitive cure for this syndrome, but treatments that improve physical development can be used.
Growth hormone therapy
Women benefit greatly from treatment with growth hormone (GH), especially if started in the early stages.
However, many individual factors ultimately determine the effectiveness of treatment.
Sex hormone replacement therapy
Most affected women need treatment with estrogen and progesterone replacement therapy to; promote puberty and the development of secondary sexual characteristics.
Hormone replacement therapy usually begins at age 14, and for most women treated with estrogen and progesterone continues until menopause.
Additional treatment
Complications and apparent symptoms should be treated, for example:
- Thyroid hormone replacement therapy is used to treat women with thyroid disease.
- Hearing loss is also corrected using hearing aids.
- Inclusion in suitable social environments is necessary to improve the ability to learn and sharpen social interaction skills.
- In addition to constantly developing skills and encouraging exercise, early intervention is undoubtedly one of the most significant steps for effective treatment.
Living with Turner Syndrome
Women can still lead healthy lives, especially with proper medical care, but undergoing treatments can relieve symptoms and improve their quality of life.
In conclusion, we learned about Turner syndrome in females, its symptoms, and how to treat and live with it.
We recommend joining support groups for women with this syndrome.
In addition, talking to a professional can provide psychological support for any other challenges that they may face.