Cellulitis is a disease that causes anxiety and stress not only for the patient; but also for his family.
If neglected and not treated properly, it can cause grave complications and becomes life-threatening.
In this article; We’ll talk about cellulitis, its symptoms, and how to treat it, especially for people with diabetes.
What does cellulitis mean?
Cellulitis is a common bacterial infection that affects the skin and can be painful at times.
It initially appears red and swollen in the affected area and then begins to spread.
Cellulitis usually occurs in the lower legs, but it can also affect any area of the body or face.
It affects the superficial layer of the skin but may affect surrounding tissues.
The infection may also spread to reach the lymph nodes and bloodstream.
Symptoms
Symptoms include the following:
- Feeling of pain, tenderness, and redness in the affected area.
- A skin ulcer.
- A rapidly spreading rash.
- Tight, shiny, and swollen skin.
- A rise in the temperature of the affected skin area.
- An abscess with the appearance of pus.
- An occasional increase in body temperature.
Some symptoms may occur that mandate consulting a doctor, such as:
- Dizziness.
- Fatigue.
- Vertigo.
- Chills or sweating.
- Muscle pain.
Some symptoms indicate that the infection is spreading, for example:
- Drowsiness.
- Inactivity.
- The appearance of blisters or red streaks on the affected area.
Causes
The disease occurs due to a bacterial infection, usually Gram-positive, for example, (Streptococcus).
The bacteria can enter the skin through a cut, incision, or insect bite.
Some factors raise the risk of infection, such as;
- Weakening of the immune system, for example, patients with diabetes, leukemia, AIDS, or some medications that weaken the immune system.
- Skin diseases, such as eczema, athlete’s foot, or exposure to shingles; Which may cause cracks in the skin, through which bacteria can pass to the inside.
- Lymphedema after surgery; in the arm or leg.
- A family history of injury.
- Obesity.
- Intravenous drug use.
Cellulitis in diabetic foot
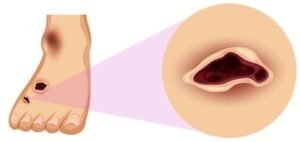
About 12-25% of diabetic patients suffer from increased risk factors that lead to a diabetic foot infection.
Diabetic patients suffer from neuropathy or motor and sensory disorders; Which causes the patient to lose his ability to distinguish between types of injuries and their pain.
Consequently, these injuries develop and result in foot ulcers that cause cellulitis.
Moreover, the lack of blood flow to the foot limits the body’s ability to fight infection.
Here comes the importance of early diagnosis and rapid intervention with treatment.
Especially that diabetic patients suffer a higher risk of lower limb amputation compared to patients without diabetes.
However, the patient can avoid possible complications by; undergoing a treatment protocol with antibiotics and following up on good wound care.
Therefore, a person with diabetes must undergo a routine examination; To check for ulcers that can affect the feet, especially the fingers, as they are the most common areas of cellulitis.
Here are some guidelines according to the recommendations of the International Working Group on Diabetic Foot (IWGDF) regarding the treatment of diabetic foot infection.
These instructions include;
- Choose the appropriate antibiotic according to the progress of the case and the severity of symptoms.
- Perform a sensitivity test before starting treatment to avoid the risks of a drug interaction.
- Evaluate and follow up on the condition after appropriate antibiotic treatment for a period ranging from 2 to 4 weeks.
- If the infection does not subside with antibiotics; Then, surgical intervention is required to control it and prevent its spread.
- If the infection extends to the bone or marrow, a culture must be performed to; determine the type of bacteria causing it and start taking the appropriate antibiotic.
Facial cellulitis
This type of infection affects the face and is the most dangerous type.
Facial cellulitis can reach the eyes and cause blindness if not treated promptly.
Orbital cellulitis affects the tissues surrounding the eyes due to infection with, Streptococcus or Staphylococcus aureus (the most common type of bacteria that causes this condition).
Children under nine years of age are infected by; only one type of bacteria at a time.
However, in adults, the infection is caused by multiple strains of these bacteria simultaneously, making them more challenging to treat.
Orbital cellulitis can also occur through a dental infection or a bacterial infection that enters the bloodstream through cuts, insect bites, or animal bites near the eye area.
Hepatic Cellulitis
Patients with liver conditions are also more prone to cellulitis.
Cirrhosis of the liver and impairment of the immune system enhance the chances of transmission of the bacterial infection that causes cellulitis.
Cellulitis generally differs in terms of etiology and diagnosis in patients with liver disease than others.
That is to say, Gram-negative bacteria; are usually the principal cause rather than Gram-positive.
Moreover, Norfloxacin prophylaxis helped reduce the risk of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP) caused by bacterial infection and cirrhosis of the liver.
It helped reduce infection rates from 61% to 7% in one year.
Studies have also proven its effectiveness in preventing the recurrence of liver disease.
The best antibiotic choice for cellulitis
Antibiotic treatment is usually considered powerful and effective.
However, the sooner we start treatment, the higher the cure rate.
There are many antibiotics of choice for treating cellulitis, for example;
- Dicloxacillin.
- Cephalexin.
- Trimethoprim.
- Sulfamethoxazole.
- Clindamycin.
- Doxycycline.
Cellulitis treatment
The doctor prescribes the appropriate treatment for the patient according to the condition and its severity.
Treatment choices include;
- Topical cream antibiotics.
- Antibiotic tablets.
- IM or IV antibiotic injections.
- Analgesics.
- Antipyretics.
- Topical antiseptics.
Home care
Some symptoms can be relieved with home care for the patient in some simple ways, such as:
- Elevate the affected limb to reduce swelling.
- Move the joints from time to time to avoid stiffness.
- Drink plenty of fluids.
- Avoid compression stockings.
- Take nutritional supplements and vitamins necessary to raise the immune system efficiency.
Further, if there is pus in the wound, then surgical intervention is required to remove it.
In conclusion, you should consult your doctor immediately if one of the symptoms of cellulitis appears.
This; Is particularly important to control inflammation and not exacerbate symptoms.
Especially; if you suffer from an immune system disorder or diabetes.
Read also